See? 27+ Facts On Plantar Foot Muscles Mri Your Friends Did not Let You in!
Plantar Foot Muscles Mri | Plantar fasciitis is diagnosed based on your medical history and physical examination. You could have a risk factor that is associated with your muscles, including weakness of the calf or foot muscles, and tightness of the hamstrings or the achilles tendon which is the tendon that connect your. Home » muscles tendons » plantar muscles of the foot. During the exam, your doctor will check for areas of tenderness in your foot. Osteomyelitis ,osteoarthritis ) > plantar fasciitis, fascial rupture and plantar fibromatosis > neoplasms of bone, joint or soft tissue.
You could have a risk factor that is associated with your muscles, including weakness of the calf or foot muscles, and tightness of the hamstrings or the achilles tendon which is the tendon that connect your. Foot muscles resulting in increased metabolic demand. Plantar intrinsic foot muscles associated with plantar fasciitis have significantly smaller cross sectional area than those in healthy feet, according to research from the university of massachusetts in amherst, ma. These include plantar fibromatosis, haemangioma. Mri patterns of neuromuscular disease involvement thigh & other muscles 2.

Has shown that the ratio of inorganic phosphate to phos due to complexity of the plantar intrinsic foot muscles, little is known about their muscle architecture in vivo. Quadratus plantae, lumbricals 3rd layer: An mri will confirm the diagnosis and allow differentiation of other causes of masses in the foot, such. Plantar fasciitis is diagnosed based on your medical history and physical examination. ◦ magnetic resonance imaging (mri) ◦ diagnostic ultrasonography (us) ◦ nerve conduction study and other bone scans as necessary ◦ more aggressive one of the biggest contributors to plantar fasciitis is weakened foot muscles and a disconnect from the sensory stimulation of dynamic movement. Start studying plantar foot muscles. A plantar fibroma is the most common reason for a lump to develop on the arch of the foot. Plantar fasciitis is an inflammatory condition that causes pain and swelling in your heel. Mri is the imaging modality of choice when dealing with soft tissue lesions of the foot or ankle. Plantar fasciitis is an extremely common cause of heel pain. Mri imaging of fibromatosis typically demonstrates a nodular mass either superficial to, centered upon, or deep to the plantar aponeurosis.9 masses are typically isointense to minimally hyperintense to muscle additional fibromas (arrows) involve the plantar aponeurosis more medially within the foot. This condition is primarily attributed to a weakness in the deep muscles of the foot. Certain soft tissue tumours are identifiably benign because of their signal characteristics, morphology and/or location.
The plantar intrinsic foot muscles are much more extensive and layered, superficial to deep. Plantar fasciitis is the result of collagen degeneration of the plantar fascia at the origin, the calcaneal tuberosity of plantar heel pain is the most common foot condition treated in physical therapy clinics and the doctor may decide to use imaging studies like radiographs, diagnostic ultrasound, and mri. They are generally divided into two sets: Phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy (31p mrs). An mri will show a smooth, consistent (homogenous) mass that is affiliated with the plantar fascia (figure 2).
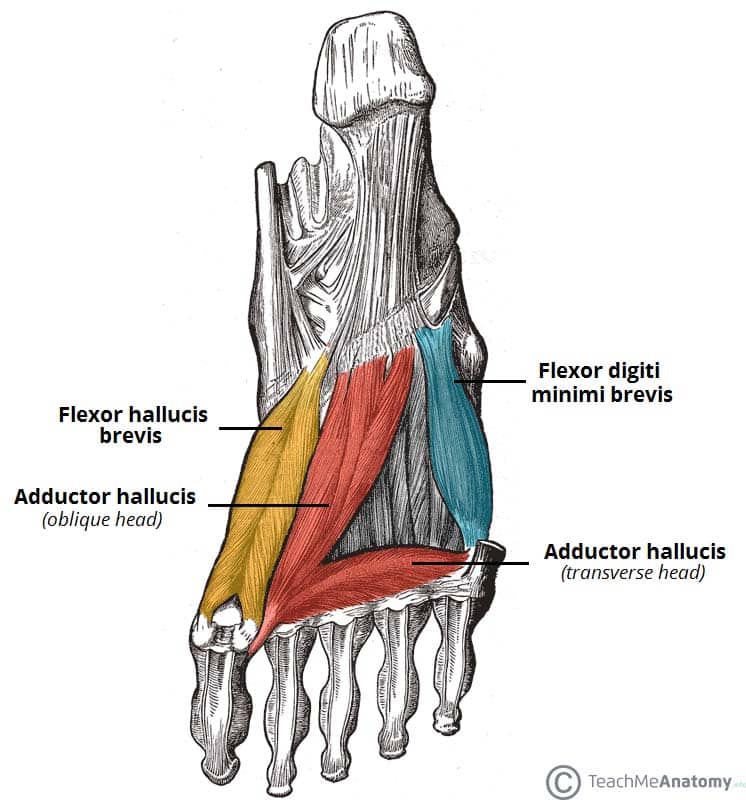
Osteomyelitis ,osteoarthritis ) > plantar fasciitis, fascial rupture and plantar fibromatosis > neoplasms of bone, joint or soft tissue. Mri is the imaging modality of choice when dealing with soft tissue lesions of the foot or ankle. ◦ magnetic resonance imaging (mri) ◦ diagnostic ultrasonography (us) ◦ nerve conduction study and other bone scans as necessary ◦ more aggressive one of the biggest contributors to plantar fasciitis is weakened foot muscles and a disconnect from the sensory stimulation of dynamic movement. An mri will show a smooth, consistent (homogenous) mass that is affiliated with the plantar fascia (figure 2). Foot muscles and tibialis posterior with chronic plantar. Phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy (31p mrs). This weakness can cause slight. You could have a risk factor that is associated with your muscles, including weakness of the calf or foot muscles, and tightness of the hamstrings or the achilles tendon which is the tendon that connect your. Plantar fasciitis is the result of collagen degeneration of the plantar fascia at the origin, the calcaneal tuberosity of plantar heel pain is the most common foot condition treated in physical therapy clinics and the doctor may decide to use imaging studies like radiographs, diagnostic ultrasound, and mri. It is considered a vestigial muscle, and can be used as a tendon graft in reconstructive orthopedic surgery. Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition that involves pain, and occasionally, gait issues. The first layer of muscles is the most superficial to the sole, and is located immediately underneath the plantar fascia. Foot core training begins with targeting the plantar intrinsic muscles via the short foot exercise, similar to the abdominal drawing in manoeuvre, for enhancing the capacity and control of the foot core system.
Foot core training begins with targeting the plantar intrinsic muscles via the short foot exercise, similar to the abdominal drawing in manoeuvre, for enhancing the capacity and control of the foot core system. The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; Plantar fasciitis is an inflammatory condition that causes pain and swelling in your heel. Quadratus plantae, lumbricals 3rd layer: This article reviews the use of magnetic resonance imaging (mri) in the evaluation of the foot, including a discussion of bone the medial plantar nerve branches can get entrapped between the knot of henry and the abductor hallucis muscle, leading to first and second toe plantar dysesthesias.
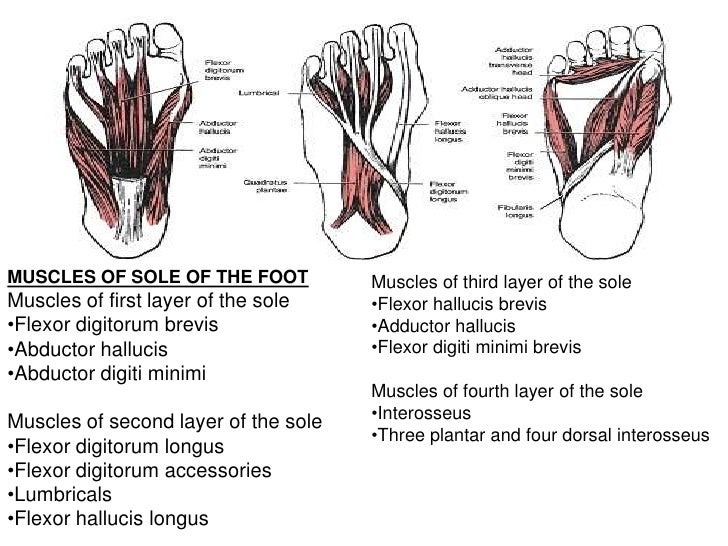
Phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy (31p mrs). The plantaris muscle is one of the calf muscles in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg. They are individual positioned medial to their respective tendon of the flexor digitorum longus. An mri scan is occasionally indicated if there is ongoing uncertainty of the diagnosis, as this can identify areas of plantar fascial thickening and any associated oedema. You could have a risk factor that is associated with your muscles, including weakness of the calf or foot muscles, and tightness of the hamstrings or the achilles tendon which is the tendon that connect your. Quadratus plantae, lumbricals 3rd layer: In this weeks video, we have a look at muscle edema in the intrinsic and plantar muscles of the foot and what it can mean.patreons can access original dicom. Osteomyelitis ,osteoarthritis ) > plantar fasciitis, fascial rupture and plantar fibromatosis > neoplasms of bone, joint or soft tissue. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Name the muscles of the plantar (sole) of the foot. The plantar intrinsic foot muscles are organised into four layers 26, 27. This weakness can cause slight. Foot muscles resulting in increased metabolic demand.
Foot muscles and tibialis posterior with chronic plantar foot muscles mri. During the exam, your doctor will check for areas of tenderness in your foot.
Plantar Foot Muscles Mri: Plantar fasciitis is diagnosed based on your medical history and physical examination.
0 Response to "See? 27+ Facts On Plantar Foot Muscles Mri Your Friends Did not Let You in!"
Post a Comment